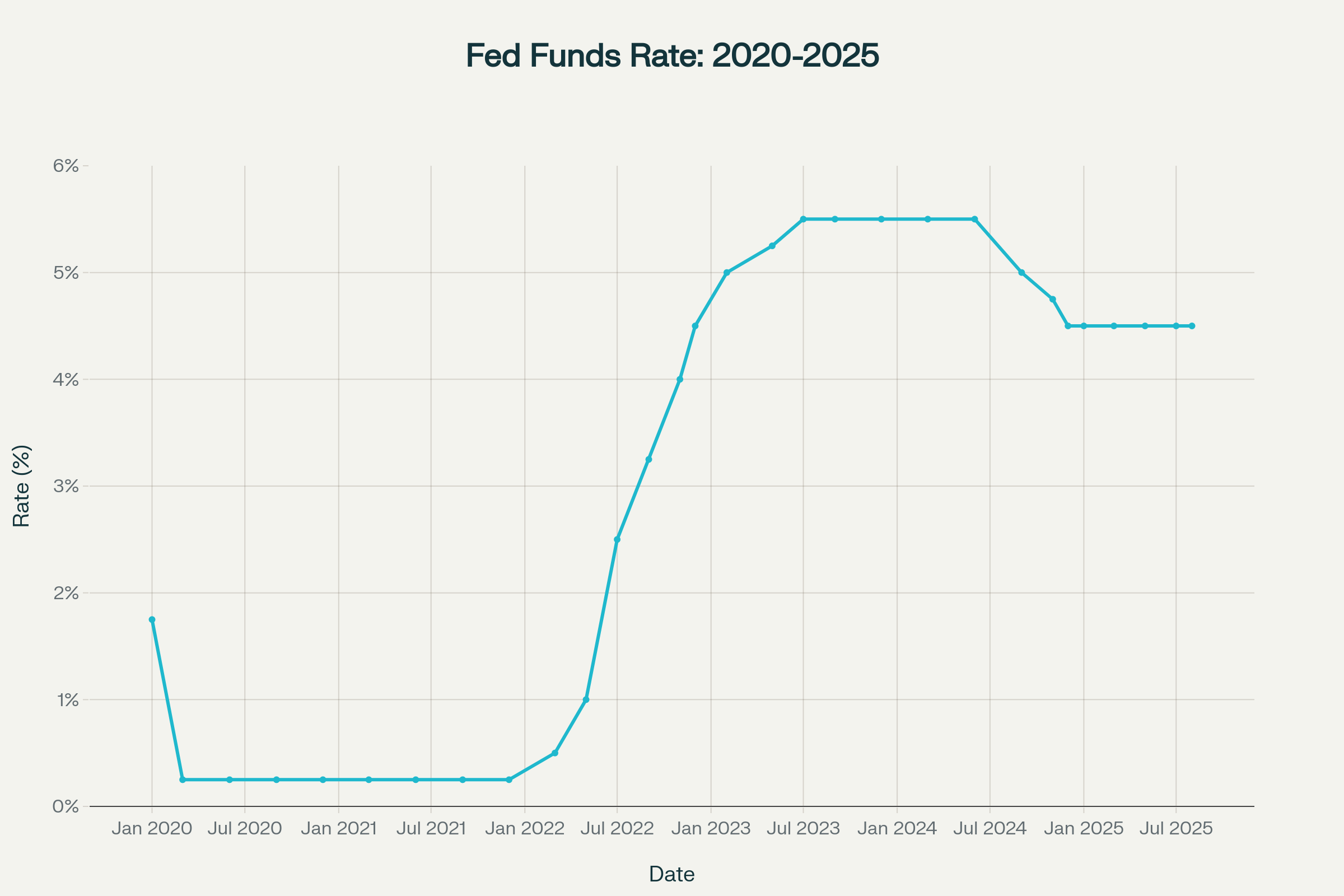
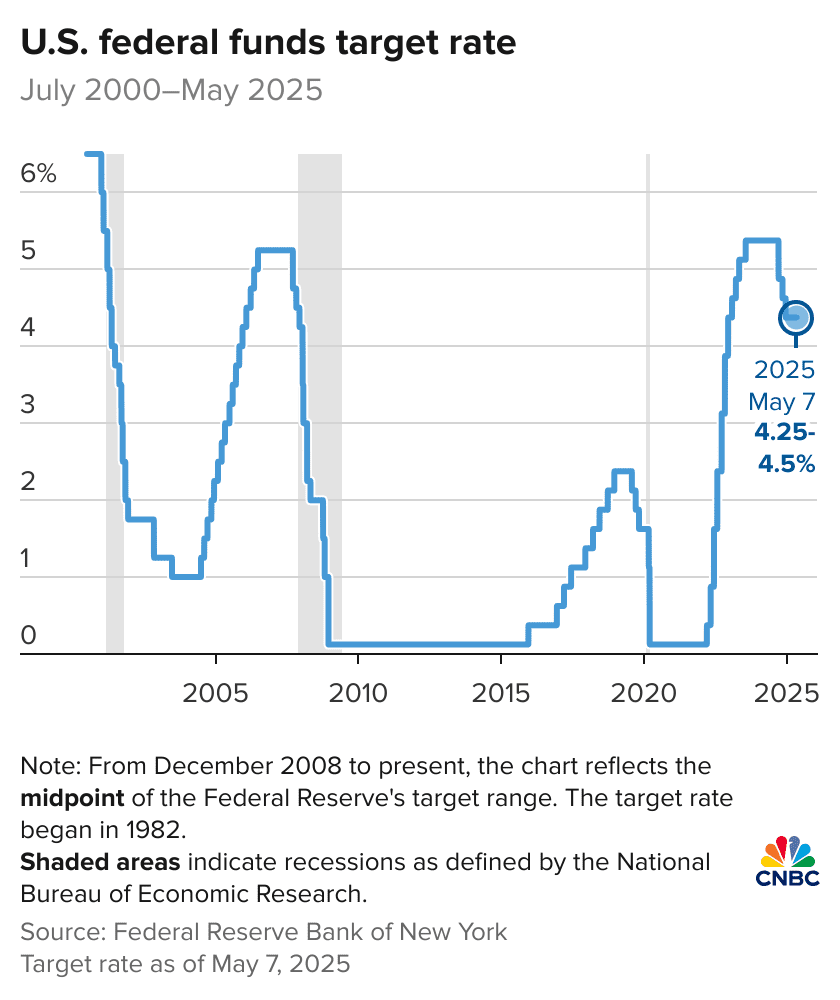
The Federal Reserve finds itself at a critical juncture in 2025, balancing persistent inflationary pressures, uncertain trade policy impacts, and unprecedented political pressure from the Trump administration. After holding the federal funds rate at 4.25%-4.50% for five consecutive meetings through July 2025, the central bank is facing mounting calls for rate cuts while grappling with complex economic headwinds, a complete fed policy 2025.

Current Policy Stance and Recent Developments
July 2025 FOMC Decision: A House Divided
The Federal Reserve’s July 29-30, 2025 meeting marked a significant turning point in monetary policy deliberations. While the Federal Open Market Committee voted 9-2 to maintain the federal funds rate at its current range of 4.25%-4.50%, the meeting was notable for its first dual dissent since 1993.
Fed Governors Christopher Waller and Michelle Bowman, both Trump appointees, broke ranks with the majority to advocate for a 0.25 percentage point rate cut. This unprecedented disagreement within the committee reflects deeper tensions about the appropriate policy response to current economic conditions.
Chairman Powell’s Measured Approach
Fed Chair Jerome Powell emphasized during his post-meeting press conference that the economy remains “in a solid position” with unemployment at 4.1% and the labor market “at or near maximum employment”. However, he acknowledged that economic activity has “moderated in the first half of the year,” with GDP growth averaging just 1.2% compared to 2.5% in 2024.
Powell stressed the Fed’s cautious stance regarding tariffs, noting that policymakers are “still a ways away from seeing where things settle down” regarding trade policy impacts. This uncertainty has contributed to the Fed’s decision to maintain what Powell characterizes as a “modestly restrictive” monetary policy stance.

Economic Backdrop: Inflation and Labor Market Dynamics
Inflation Remains Elevated
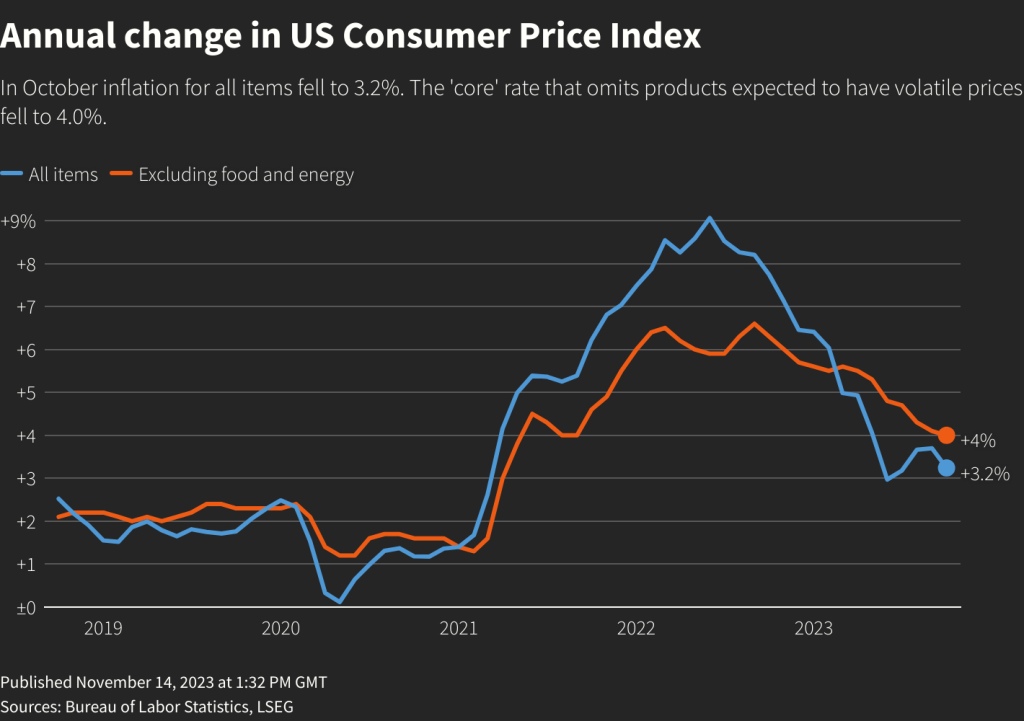
Despite significant progress since the 2022 peak of over 11%, inflation continues to run above the Fed’s 2% target. The Consumer Price Index rose to 2.7% year-over-year in June 2025, while core CPI reached 2.9%. More concerning for Fed officials, the central bank’s preferred measure – core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) inflation – stands at 2.8%, unchanged from the 2024 average.
The persistence of elevated inflation reflects several factors, including:
- Tariff-induced price pressures: Early signs suggest that Trump administration tariffs are beginning to filter through to consumer prices, particularly in goods categories like furniture, appliances, and toys
- Services inflation stickiness: Housing and other services continue to contribute to overall price pressures
- Wage growth moderation: While wage growth has continued to slow, it remains above levels consistent with 2% inflation
Labor Market: Strong but Showing Cracks
The labor market presents a complex picture that has contributed to the Fed’s cautious approach. While the unemployment rate remains low at 4.2%, recent data suggests emerging weakness:
- July payroll growth came in at just 73,000 jobs, well below expectations of 110,000
- Significant downward revisions to May and June employment data totaling 258,000 jobs
- Job creation has averaged 150,000 per month over the past three months, a notable slowdown
This labor market softening has provided ammunition for the Fed’s dovish members who argue for preemptive policy easing.
The Tariff Challenge: A New Complication for Monetary Policy
Policy Uncertainty and Economic Impact
President Trump’s tariff policies have introduced a significant new variable into the Fed’s decision-making calculus. The central bank faces the challenge of distinguishing between temporary, one-time price level increases from tariffs versus persistent inflationary pressures that would require continued restrictive monetary policy.
Fed Analysis of Tariff Effects
According to the Fed’s Monetary Policy Report to Congress, “the effects of import tariff increases this year on U.S. consumer prices are highly uncertain, as trade policies continue to evolve, and it is still too early to assess how consumers and businesses will respond”. The report notes that while tariff effects are not directly visible in official consumer price data, price movements across various goods categories suggest tariffs may have contributed to recent goods inflation increases.
Regional Fed Perspectives
Minneapolis Fed President Neel Kashkari has noted that tariff uncertainty led to “the biggest sudden drop in confidence in the past decade except for when COVID-19 hit” in March 2020. This loss of confidence could potentially have larger economic effects than the tariffs themselves, as businesses and consumers pull back from spending and investing.
Monetary Policy Implications
The tariff situation has raised the bar for both rate cuts and increases. As Kashkari noted, “the hurdle to change the federal funds rate one way or the other has increased due to the tariffs”. This reflects several key considerations:
- Inflation Expectations Risk: Given the paramount importance of keeping long-run inflation expectations anchored, the bar for cutting rates even in the face of economic weakness is higher
- Neutral Rate Impact: Tariffs likely push down the near-term neutral interest rate (r*) by reducing investment demand and increasing uncertainty
- Policy Timing: The Fed appears willing to wait for more clarity on both tariff implementation and economic effects before adjusting policy stance
Political Pressures and Fed Independence
Trump Administration Pressure Campaign
The Federal Reserve has faced an unprecedented level of political pressure from the Trump administration throughout 2025. President Trump has repeatedly called for aggressive rate cuts, at one point demanding the federal funds rate be reduced to 1%. This pressure campaign has included:
- Public criticism: Trump has characterized Fed policy as “killing growth” and labeled Powell a “moron”
- Direct engagement: Trump made an unusual visit to Fed headquarters to tour renovation projects, which administration officials have suggested could be grounds for dismissal
- Appointee influence: The dissenting votes from Trump-appointed governors Waller and Bowman reflect the administration’s policy preferences
Fed Response and Independence
Despite intense political pressure, Powell and the Fed majority have maintained their commitment to data-dependent policy making. Powell has consistently argued that the current policy stance is appropriate given economic conditions, emphasizing the Fed’s dual mandate of price stability and maximum employment. role of central banks
Legal experts note that Fed officials can only be removed “for cause,” providing some protection from political interference. However, the political dynamics have added complexity to an already challenging policy environment.
Market Expectations and September Outlook
Shifting Rate Cut Probabilities
Following the disappointing July jobs report, market expectations for a September rate cut have surged dramatically. According to the CME FedWatch tool, the probability of a 0.25 percentage point rate cut at the September 16-17 FOMC meeting has jumped to over 90%, up from around 40% immediately following the July meeting.
This shift reflects several factors:
- Weakening labor market data: The July jobs report and revisions to prior months suggest greater labor market softness than previously recognized
- Dovish commentary: Additional Fed officials, including San Francisco Fed President Mary Daly and Minneapolis Fed President Neel Kashkari, have made more dovish comments in recent days
- Dual dissent significance: The unprecedented dual dissent in July suggests growing internal pressure for policy easing
Jackson Hole Symposium: A Key Signal
Market participants are closely watching the upcoming Jackson Hole Economic Symposium, scheduled for August 21-23, 2025, with the theme “Labor Markets in Transition: Demographics, Productivity, and Macroeconomic Policy”. Powell’s speech at this annual gathering is traditionally used to signal major policy shifts, and expectations are high that he may provide clearer guidance on the September decision.
Last year, Powell used his Jackson Hole speech to signal the Fed’s readiness to begin cutting rates, making this year’s address particularly significant given current economic crosscurrents.

Looking Forward: Policy Challenges and Considerations
The Balancing Act Ahead
As the Federal Reserve navigates the remainder of 2025, policymakers face several key challenges:
1. Inflation vs. Employment Trade-offs
The Fed must balance persistent above-target inflation against growing signs of labor market weakness. The dual dissent in July highlighted these competing concerns, with dissenters arguing that tariff-driven inflation should be viewed as temporary while employment risks are mounting.
2. Tariff Policy Evolution
The ultimate scope and duration of the Trump administration’s tariff policies remain uncertain, complicating the Fed’s ability to forecast their economic impact. Powell has emphasized that it’s “still early to assess” these effects comprehensively.
3. Political Independence
Maintaining credible independence while operating under intense political pressure represents an ongoing challenge. The Fed’s ability to make purely data-driven decisions may be tested as the 2025 progresses. how the fed sets rates
Baseline Scenario and Risks
Most economists expect the Fed to begin cutting rates in September, with market pricing suggesting 1.5-2.0 percentage points of total easing through 2025. This baseline assumes:
- Continued labor market softening without recession
- Inflation moving gradually toward the 2% target
- No major escalation in trade tensions
However, significant risks exist in both directions. Stronger-than-expected inflation or renewed tariff pressures could delay cuts, while sharp economic deterioration could prompt more aggressive easing.
The Federal Reserve enters the critical final months of 2025 facing its most complex policy environment in years. The dual challenges of persistent inflation and emerging labor market weakness, complicated by tariff uncertainty and political pressure, require careful navigation of competing risks.
The July meeting’s dual dissent signals growing internal debate about policy direction, while market expectations for September action reflect confidence that economic data will ultimately drive Fed decisions. Powell’s upcoming Jackson Hole address may provide crucial clarity on the central bank’s thinking as it seeks to achieve its dual mandate while maintaining credibility and independence.
The stakes are high: getting the timing and magnitude of policy adjustments right will be crucial for maintaining economic stability and the Fed’s hard-won credibility in the fight against inflation. As Powell emphasized, everything the Fed does is “in service to our public mission” of achieving maximum employment and price stability. How well the central bank executes this mission in the coming months will have lasting implications for both the U.S. economy and the institution of independent monetary policy.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter for Exclusive Updates and Insights
By subscribing, you’ll gain access to a treasure trove of valuable content delivered straight to your inbox. Stay ahead of the curve with expert articles, insider tips, and thought-provoking resources carefully curated by our team of professionals. Whether you’re a seasoned enthusiast or just getting started, our newsletter is a must-have resource for staying informed and inspired.
-
Fed Policy 2025: Rates, Dissent & Tariff FalloutThe Federal Reserve finds itself at a critical juncture in 2025, balancing persistent inflationary pressures, uncertain trade policy impacts, and unprecedented political pressure …
-
Navigating Supply Chain Disruptions Amid New Tariff Wars in 2025The global trade landscape in 2025 is increasingly volatile, with new tariff wars disrupting supply chains worldwide. The United States has imposed tariffs …
-
Gold Surges Past $2,800: Is It Time to Reassess Your Strategy?Gold prices have surpassed the key $2,800 mark for the first time, driven by global economic uncertainty and renewed safe-haven demand amid escalating …
-
February 2025 | Forex OutlookAs we enter February 2025, the forex market remains dominated by a strong US dollar, with major currencies like the euro potentially oversold …
-
Navigating Forex in 2025Geopolitical tensions have emerged as a significant driver of currency fluctuations in 2025, creating both opportunities and risks for forex traders. As reported …
-
The Impact of AI Innovations on US Tech Stocks: Lessons from the Nvidia Sell-OffArtificial intelligence (AI) has become the driving force behind technological advancements, transforming industries and fueling the rapid rise of US tech stocks. However, …
